What is Azure Service Bus?
Azure Service Bus is a message broker service that is hosted on the Azure platform and it provides functionality to publish messages to various applications and also decouple the applications.
According to Microsoft documentation,
Microsoft Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise integration message broker. Service Bus can decouple applications and services. Service Bus offers a reliable and secure platform for asynchronous transfer of data and state.
Data is transferred between different applications and services using messages. A message is in binary format and can contain JSON, XML, or just text.
Microsoft service bus comes in different flavors,
- Queues
- Topic (we will cover this in the next articles)
Azure Service Bus Queues
Queues follow a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) pattern. Queues provide one-way transport the sender is going to send the message in the queue and the receiver collects messages from the queue. In queues, there is a 1:1 relationship between the sender and receiver. Messages are present in the queue until the receiver processes and completes the messages.

The queue contains a secondary sub-queue, called a dead-letter queue (DLQ). Whenever we create a queue DLQ is automatically added in our main queue. When the messages are not delivered to the receiver or cannot be processed by the receiver then such messages are pushed to DLQ.
Now we have discussed enough regarding Queues so let's create queues in Azure and build a simple application to send and receive messages from the queue.
Creating a simple application to send and receive messages from the queue.
Prerequisites
- Azure account(If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free trial account).
- Basic knowledge of Asp.net Core Web API
Overview of the application
We will be creating a simple application which consists of 3 parts,
- Create Azure Service Bus Queue using Azure Portal (Covered in this article)
- Create Web API to push the message into Queue (Covered in this article)
- Create a Background Service to receive a message from Queue (Covering in Part 2)
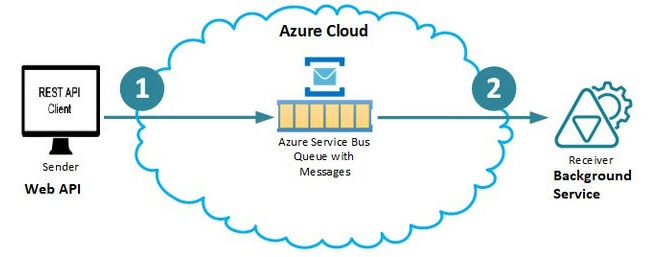
- Creating Azure Service Bus Queue using Azure Portal
- Login to Azure and click on the Create a Resource button.
- In the search box type service bus and select it.
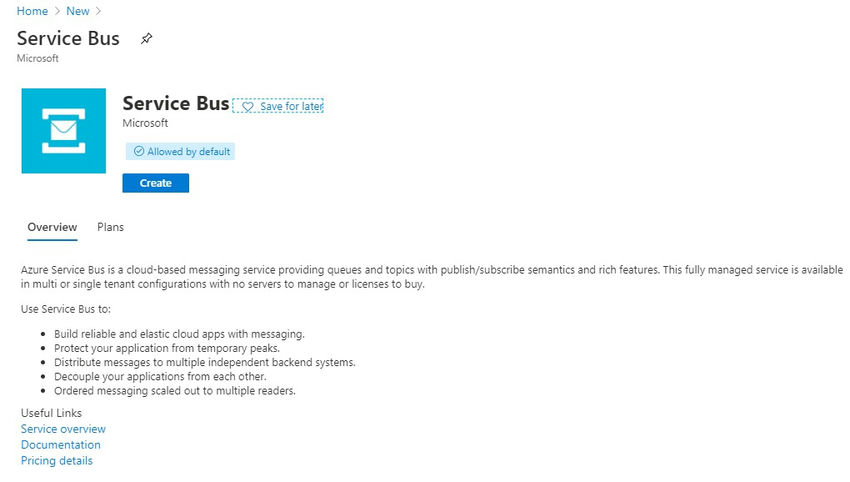
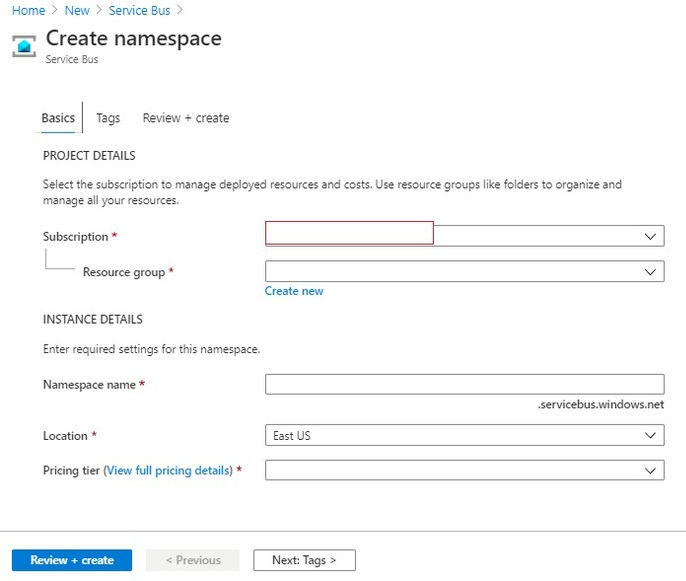
- Click on the Create button. You will see the Create Namespace page.
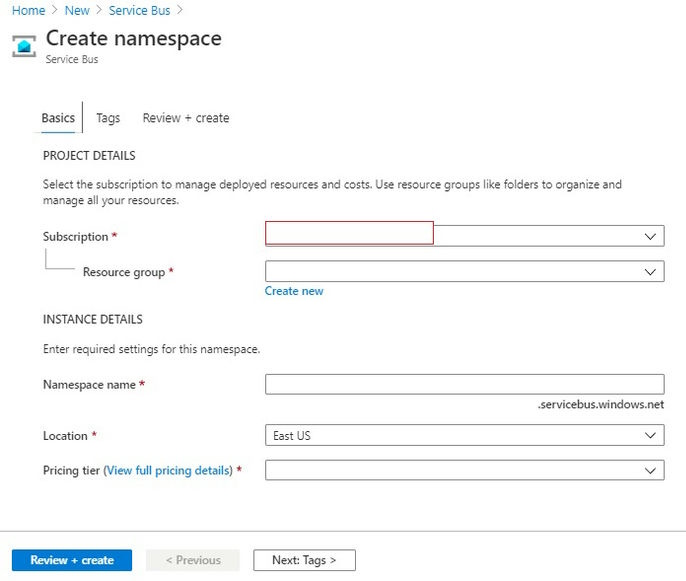
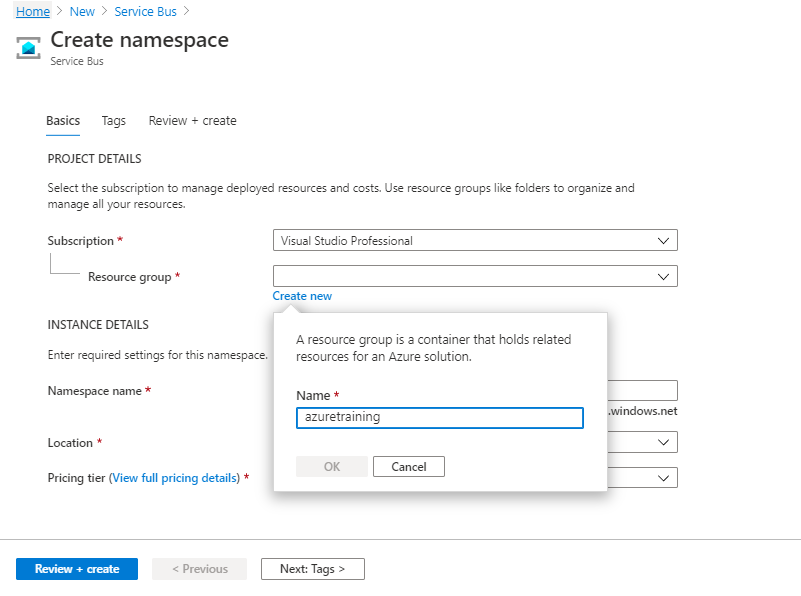
- Azure has Resource Groups (RG) which acts as a container for your resources. So now we are going to create a Service bus resource. First, we need to create a Resource Group. If you have already created RG then you can use the same here. Under Resource group click on Create New button and give a unique RG name.
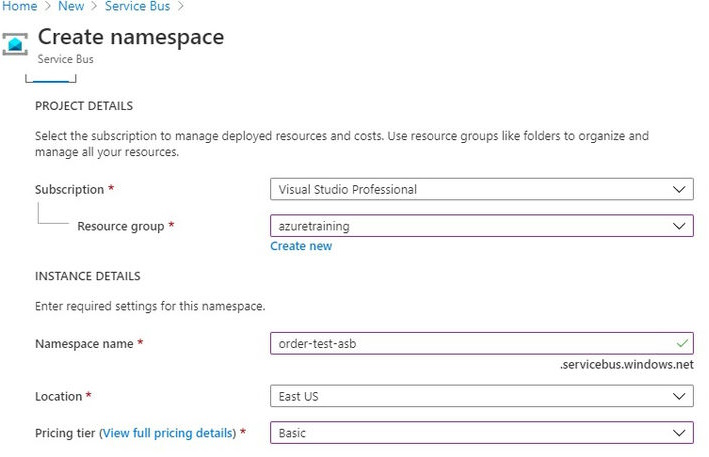
- Now we have to specify the Namespace name. A namespace is a container for all messaging components. Multiple queues and topics can be in a single namespace, and namespaces often serve as application containers.
- Select the location.
- Select pricing tier. Azure provides 3 pricing tiers,
- Basic
- Standard
- Premium
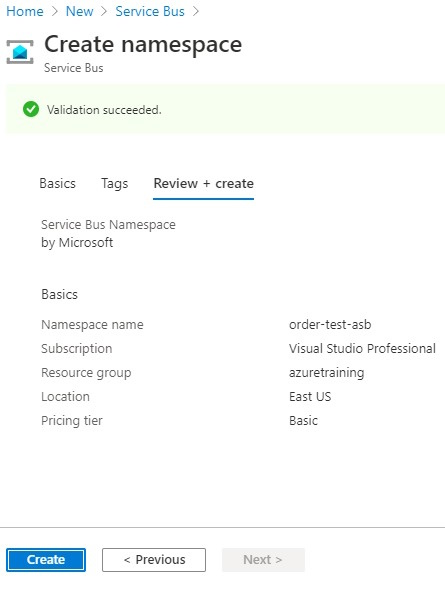
- We have filled in all details so click on the Review + Create button.
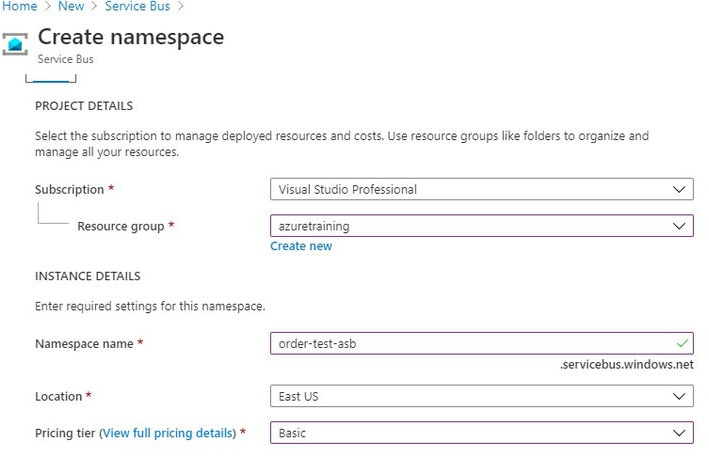
- Review everything is added property and finally click on the Create button.
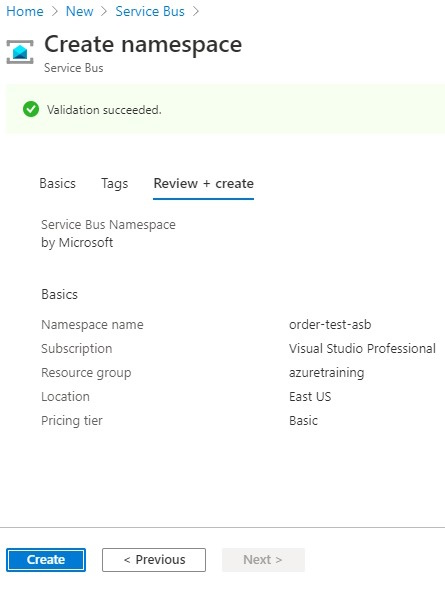
- Creating resources will take time.
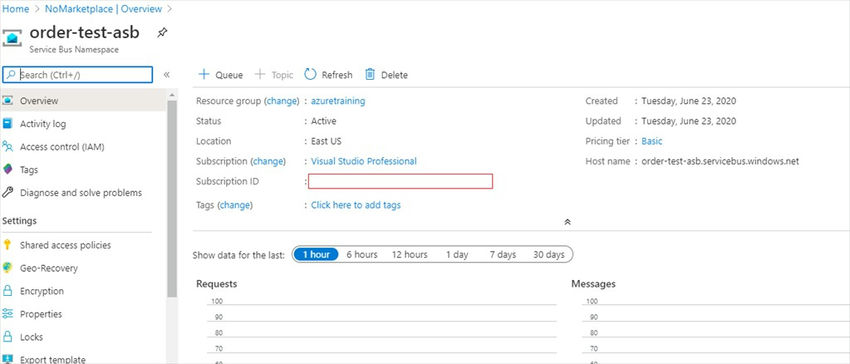
- Now our order queue is created successfully.
- Go to the Queues section in the left panel click on Queue give a unique name for the queue and click on the Create button.
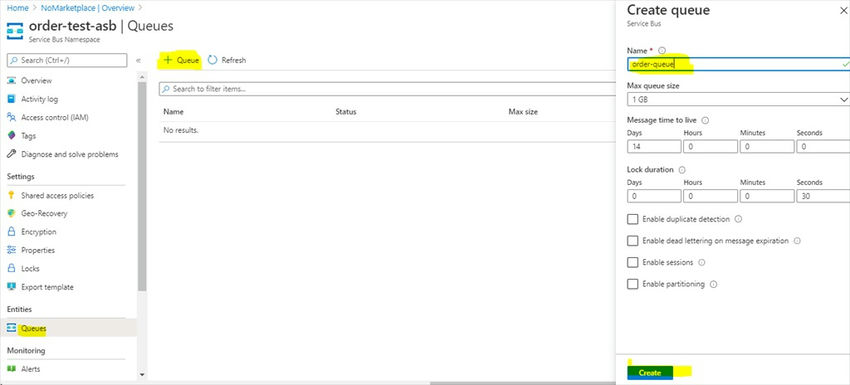
That's it. We have created our first queue.
Create Web API to push the message into Queue
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 19(if you are using .NET Core 3.1)
- .NET Core 3.1 SDK installed
The first thing is to create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project. For those who are new to ASP.NET Core, I have listed down the steps to create a new Web API project.
- Open Visual Studio and click on File -> New -> Project. Then select ASP.NET Core Web Application and click on the Next button.
- Give the project name and click on the Create button.
- After that select API and click on Create button.
- So now your ASP.NET Core Web API project is set up.
- First, we need to install the Azure Service Bus NuGet package.
Create a new class called Order.cs and add below properties,
To interact with Azure Service Bus Microsoft.Azure.ServiceBus package provides something called QueueClient which accepts queue connection string and queue name as input and returns the QueueClient object. First, we grab the connection string of Queue from Azure Portal. So open the queue and click on Shared access policies then select RootManageSharedAccessKey and copy it into the appsettings.json file.
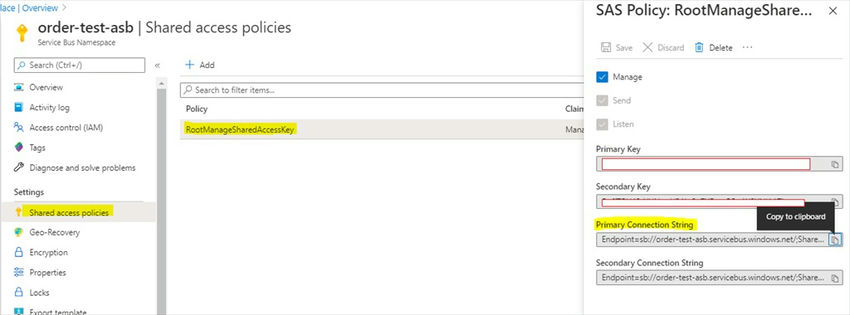
appsettings.json
Create a new controller called OrdersController and add the below code to push messages into the queue,
So we created the QueueClient object and then we created Message. We used the SendAsync() method to push messages to the queue.
We are testing this using Postman. Run the app and hit post API to push the order into Queue.

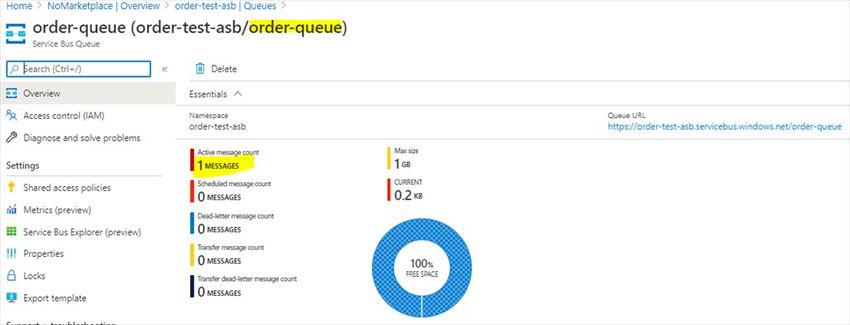
After a successful POST call let's go to Azure Portal and see if the message is pushed to the queue. So we have 1 active message in the queue.
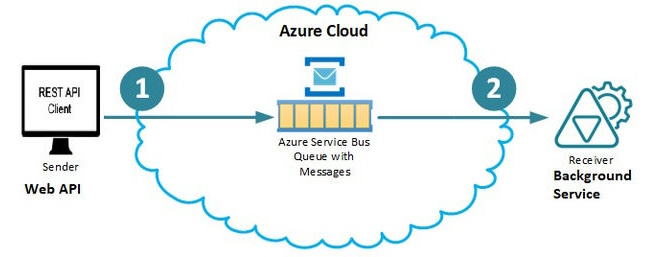
The azure service bus is a fully managed message integration broker. If two applications want to communicate with each other with less dependency, then the Azure service bus can used to send and receive the messages between them. It can provide your application decoupling and asynchronization with great flexibility as the two applications have less dependency on each other. Azure service message is reliable and durable as well. You can send a small text message or a complex message (object) to the message queue.
What we are going to cover.
- How to create a service bus and queue in Azure.
- How to send/receive messages from Azure service bus queue using C# code.
- How to run applications with this code.
How to create a service bus and queue in Azure (short intro as it can be viewed in Azure sites)
- Log in to the Azure portal and navigate to the service bus.
- Now click on the add button to create a namespace.
You can choose a resource group or create a new resource group. Add the namespace and the location at your convenience.
Now there is an option of Pricing Tier. For this application, I have used Basic for learning purposes.
And fill in some other details in the tab and create the namespace. It will take some time and now we are ready to create a Queue.
Now open the newly created service bus namespace and create the queue.
After creating the namespace and the queue we need to create the claims and policies for the service bus namespace. Create a shared access policy for the service bus namespace.
There are 3 types of claims in shared access policy and one can apply all three claims to one policy or combine any two. But as per the application needs, I suggest you create a policy based on the responsibilities.
Claims
- Managed: Queue creation and deletion can be done with this claim
- Send: Only Message sending can be done with this claim
- Listen: Only Message received can be done using this claim
How to send/receive messages from the Azure service bus queue using the C# code:
Generally, in ideal situations, one application (sender) is responsible for sending messages to the queue and another application (receiver) listens to the queue. If any message is available in the queue it reads the message from the queue and marks/removesit. Microservices applications are the best suitable solution for the service bus.
In the article, I have used .net core(2.1) and C# code to demonstrate the Azure service bus console application. I am using Visual Studio 2017. Only sending and receiving messages will be the part of this article, the creation of queue using C# code is not included.
There are 3 parts to the console application.
Entry point of the application (of course the main method in Program class).
Code for Program.cs
The main method (entry point) calls two methods; e.g. GetMessageFromQueue() and PutMessageInQueue().
GetMessageFromQueue() method creates the ServiceBusReceiver object and invokes the Listener method.
PutMessageInQueue() creates the ServiceBusSender object and invokes the SendMessage method.
Inside putMessageInQueue() there is do..while loop. It is needed to prompt the user to type the message that he wants to send to the Queue. After sending the message in the queue, the user can terminate the program by pressing the END key or send another message by pressing the ENTRY key.
ServiceBusSender class
It will take the text message prepare the payload and send it to the Queue. Note that, it will be having Azure shared access policy.
Code for ServiceBusSender.cs
ServiceBusReceiver class
It will listen to the queue and trigger the message handler method if there is any message available in the Queue. It will have Azure shared access policy.
Code ServiceBusReceiver.cs




No comments:
Post a Comment